Development & Testing
Critical technologies used by all UNAVCO supported projects, such as GNSS receivers and antennas, data communications, and power systems are rapidly evolving. Meeting project requirements for optimal system design, performance, and financial constraints requires dedicated expertise and coordination with sponsors, community members, and hardware manufacturers. UNAVCO's Development and Testing (D&T) staff provide analysis of power systems, data communications devices, and next-generation GNSS systems in order to evaluate new features and to examine system performance. In addition, D&T closely collaborates with the GDS on the ongoing development of teqc software to integrate new GNSS constellation capabilities.
As new GNSS constellations become operational and require next generation antenna/receiver systems that are orders of magnitude more complex than current models the D&T staff will continue providing updated analysis of their potential for scientific applications. Our community's increased reliance on real-time and high-rate data requires frequent evaluation of new data communications systems for bandwidth, robustness, and latency. Expansion of polar services requires development of systems better able to withstand harsh environmental conditions with lower power draw in order to deliver uninterrupted data year-round. Recent large earthquakes in Japan and Chile made clear the need to ensure that GPS/GNSS systems function properly during strong shaking and have uninterrupted data communications.
UNAVCO community members who would like to request D&T project support are encouraged to Request Support.
Recent D&T Publications
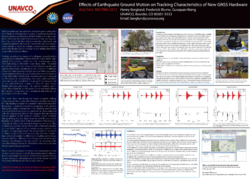
Berglund, H. T., F. Blume, and A. Prantner (2015), Effects of earthquake ground motion on tracking characteristics of new Global Navigation Satellite System receivers. Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, 3282–3288. doi: 10.1002/2015GL063539.
Langbein, John, Evans, J.R., Blume, Fredrick, and Johanson, Ingrid, 2014, Response of Global Navigation Satellite System receivers to known shaking between 0.2 and 20 Hertz: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2013-1308, 28 p., http://dx.doi.org/10.3133/ofr20131308.
Wang, G., F. Blume, C. Meertens, P. Ibanez, and M. Schulze (2012), Performance of high-rate kinematic GPS during strong shaking: Observations from shake-table tests and the 2010 Chile earthquake, J. Geod. Sci., 2, 15–30.
Recent D&T Activities
| Title | Summary | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
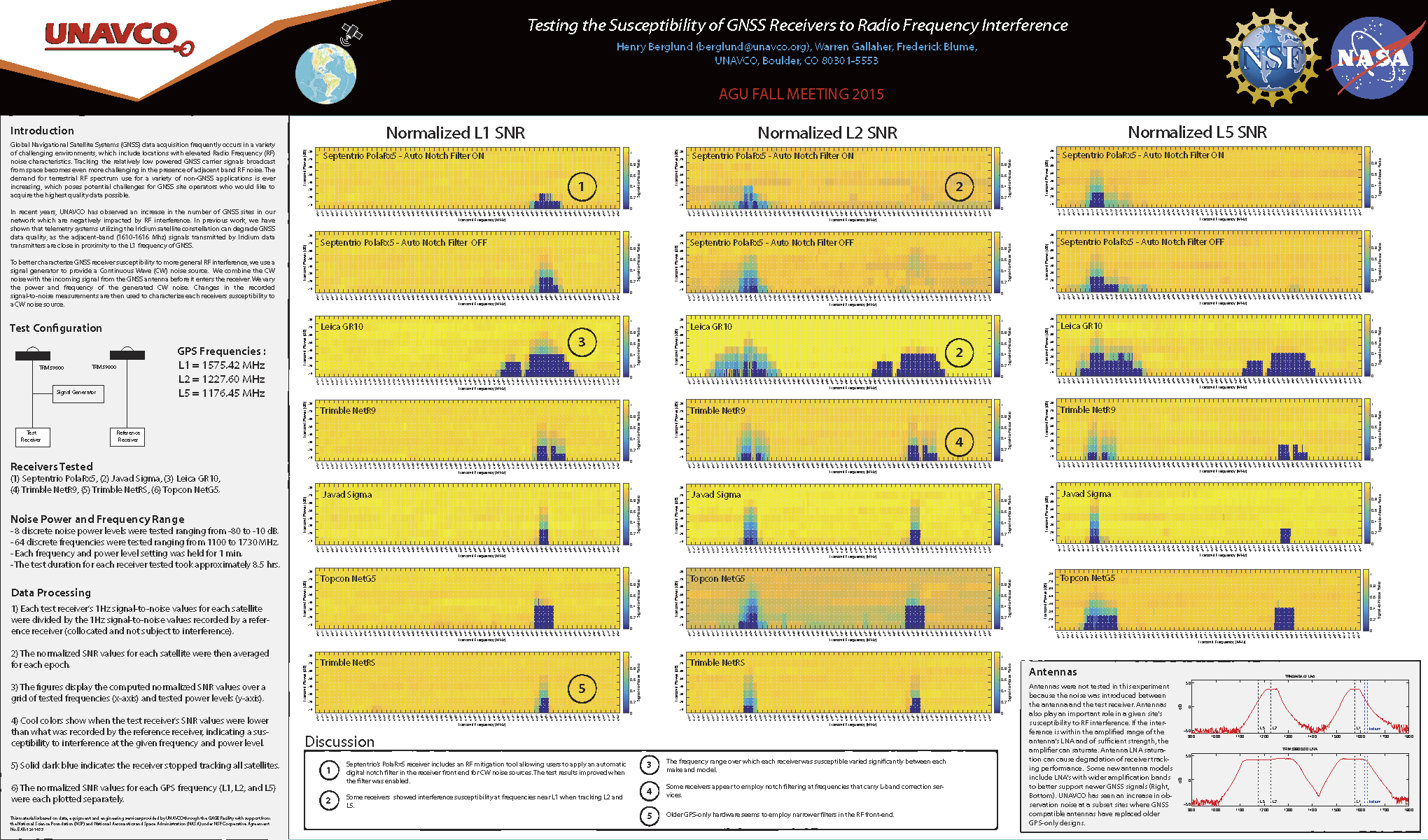
Testing the Susceptibility of GNSS Receivers to Radio Frequency Interference | To better characterize GNSS receiver susceptibility to more general RF interference, we use a signal generator to provide a Continuous Wave (CW) noise source. We combine the CW noise with the incoming signal from the GNSS antenna before it enters the receiver. We vary the power and frequency of the generated CW noise. Changes in the recorded signal-to-noise measurements are then used to characterize each receivers susceptibility to a CW noise source. | 2015 |
|
Stability of GNSS Monumentation: Analysis of co-located monuments in the Plate Boundary Observatory | Geodetic-quality permanent GNSS stations have used a number of different monumentation styles for the purpose of ensuring that the motions of the GNSS antenna reflect those of the Earth's crust while minimizing non-tectonic motions near the surface. To increase the understanding of monument stability of various monument styles in diverse geologic conditions UNAVCO has constructed two additional monuments at five existing Plate Boundary Observatory stations during the past year. Deep drilled-braced, short drilled-braced, and single mast type monuments were installed at sites with bedrock at the surface; deep drilled-braced, short driven-braced and pillar type monuments were installed at sites with alluvium or soil at the surface. Sites were selected that comprised a variety of geographic, hydrologic, and geologic conditions. The resulting set of 10-meter spaced monument triangles will yield valuable information regarding the stability of their types in different settings. Sub-millimeter results from UNAVCO’s short-baseline processing efforts will be presented showing further details of monument performance site characterization. | 2014 |
|
Real-time GNSS Positioning – High-Precision Kinematic Testing | The use of high-rate and real-time GNSS measurements for hazards monitoring and scientific applications is still in its infancy and there is great potential for its integration with strain, gravity and seismic measurements. Many commercial vendors and public agencies now offer real-time positioning services that provide sub-decimeter accuracy, with some approaching the sub-centimeter level. As GNSS network operators begin transitioning into offering real-time products, they will need to consider a number of factors including but not limited to: cost, position accuracy, solution latency, network topology and bandwidth. Periodic evaluation of real-time positioning systems will need to be conducted in order to optimize their integration into hazard-monitoring and multi-disciplinary networks. Controlled outdoor kinematic and static experiments provide a useful method for evaluating real-time systems, helping to identify system limitations, and characterize performance and reliability. | 2014 |
|
Effects of the April 1st, 2014 GLONASS Outage on GNSS Receivers | The use of multi-constellation GNSS receivers has been assumed as a way to increase system integrity both by increased coverage during normal operations and fail-over redundancy in the event of a constellation failure. At aproximately 21:00 UTC on April 1st the entire GLONASS constellation was disrupted as illegal ephemeris uploaded to each satellite took effect. The outage continued for more than 10 hours as affected satellites broadcast navigation messages with incorrect application times. | 2014 |
|
UNAVCO Real-Time GNSS Positioning: High-Precision Static and Kinematic Testing of the Next Generation GNSS network | The GAGE facility, managed by UNAVCO, operates a real-time GNSS (RT-GNSS) network of ~450 GNSS stations. The majority of the streaming stations are part of the EarthScope Plate Boundary Observatory (PBO). Following community input from a real-time GNSS data products and formats meeting hosted by UNAVCO in Spring of 2011, UNAVCO now provides real-time PPP positions, and network solutions where practical, for all available stations using Trimble’s PIVOT RTX server software and TrackRT. | 2014 |

|
Trimble RTX - Preliminary Kinematic Testing | 2014 | |

|
Comparison of Real-Time Kinematic GNSS Positioning Techniques Using Moving and Stationary Antennas | The use of high-rate and real-time GNSS measurements for hazards monitoring and scientific applications is still in its infancy and there is great potential for its integration with strain, gravity and seismic measurements. Many commercial vendors and public agencies now offer real-time positioning services that provide sub-decimeter accuracy, with some approaching the sub-centimeter level. As GNSS network operators begin transitioning into offering real-time products, they will need to consider a number of factors including but not limited to: cost, position accuracy, solution latency, network topology and bandwidth. Periodic evaluation of real-time positioning systems will need to be conducted in order to optimize their integration into hazard-monitoring and multi-disciplinary networks. Controlled outdoor kinematic and static experiments provide a useful method for evaluating real-time systems, helping to identify system limitations, and characterize performance and reliability. Preliminary findings from tests using a static antenna and a comparison of real-time kinematic positioning methods will be highlighted. | 2013 |
|
Effects of Earthquake Ground Motion on Tracking Characteristics of New GNSS Hardware | Strong motion near the epicenters of recent great earthquakes such as Maule and Tohoku have resulted in tracking disruptions, hardware failures and data loss at GNSS stations. In order to optimize GNSS-based hazard monitoring and early warning systems the reasons for these failures must be understood and mitigation strategies developed. Controlled shake table experiments provide a means to evaluate various hardware components and identify failure mechanisms and shaking thresholds responsible for system failures. | 2012 |

|
UNAVCO Development and Testing Activities in Support of the IGS GNSS Mission | Highlights the teqcniques used to upgrade NASA's Global GNSS Network (GGN), D&T hardware evaluations, and future TEQC Develoment at UNAVCO. | 2012 |
|
GPS/GNSS Inteference from Iridium Data Transmitters | The Iridium satellite communication system broacasts in the 1610 to 1626.5 MHz band. The L1 frequencies broadcast by GPS, Galileo and GLONASS satellites are 1575.42 MHz, 1575.42 MHz, and 1602 MHz + n x 0.5625 MHz, respectively. The proximity of the Iridium frequency band with the L1 frequencies of the GPS, Galileo and GLONASS systems leaves GNSS receivers susceptible to interference from Iridium data transmissions. Interference from these transmissions can cause cycle slips and loss of lock on the carrier and code phases, thereby degrading the quality of GNSS observations and position estimates. | 2011 |

|
Support of EarthScope Campaigns at the UNAVCO Facility | Describes EarthScope campaign equipment, UNAVCO monumentation techniques, and projects highlights from campigns that were conducted in 2005-2011. | 2011 |

|
The Effects of L2C Signal Tracking on High-Precision Carrier Phase GPS Positioning | The L2C signal was introduced to improve the accuracy, tracking and redundancy of the GPS system for civilian users. The L2C signal also provides improved SNR data when compared with the L1 C/A-code signal. We use several different methods to determine the effect that logging L2C has on carrier phase measurements and positioning for Trimble Net RS receivers. | 2010 |
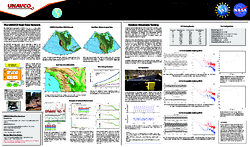
Monumentation Stability Experiment

Position time series from Plate Boundary Observatory (PBO) site P811 which is part of the Monumentation Stability Experiment. The timing of precipitation events (blue) correlates well with transient events in the station's position time series (red). During the next five years the D&T staff will be participating in the analysis of data collected by five station triplets to better characterize and understand the stability of various monument designs.
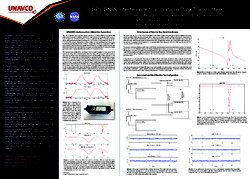
GLONASS Outage Analysis
Analysis of the impact of the April 1st, 2014 GLONASS outage on the GNSS enabled sites within the UNAVCO archive. Yellow and red circles indicate stations where receiver tracking was interrupted. (Access to the data and larger interactive maps)
Last modified: 2020-04-16 04:20:44 America/Denver

